terminal electron acceptor in fermentation|what is fermentation in chemistry : Baguio In anaerobic respiration, a molecule other than oxygen is used as the terminal . บ้านผลบอล 888 โปรแกรมบอล ผลบอลล่าสุด 888. ดูผลบอลสด 888 เป็นอีก 1 ตารางฟุตบอล ตารางแข่งบอล ที่สามารถไล่ดูช่วงเวลาการแข่งขันแต่ละทีมได้ง่าย โดยเรียง .
terminal electron acceptor in fermentation,In aerobic organisms, the terminal electron acceptor is oxygen. In anaerobic organisms, the terminal electron acceptor can vary from species to species and include but are not limited to various metals like Fe(III), Mn(IV) and Co(III), CO 2, nitrate, .In anaerobic respiration, a molecule other than oxygen is used as the terminal .what is fermentation in chemistryIn aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is an oxygen molecule, O 2.If .
terminal electron acceptor in fermentation what is fermentation in chemistryIn aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is an oxygen molecule, O 2.If .
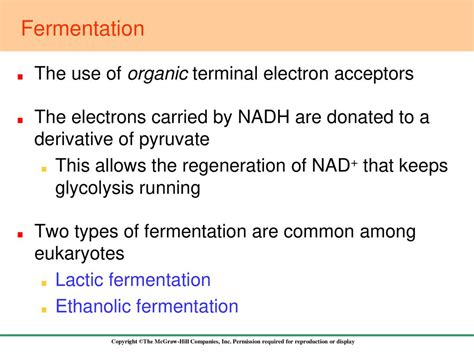
Fermentation. In fermentation, another type of heterotrophic metabolism, an organic compound rather than oxygen is the terminal electron (or .Fermentation. Some cells make ATP solely via substrate-level phosphorylation, either because they lack the electron transport chain, or because suitable terminal electrons acceptors are unavailable. They .
How is this done? In some living systems the electron transport chain (ETC) use an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor. Processes that use an organic molecule to .Their redox state and energy conservation highly depend on the availability of a terminal electron acceptor, for example oxygen in aerobic production processes. Under . Oxygen-vacancy-enabled magnetite as a terminal electron acceptor enhances acetate production from waste activated sludge in alkaline fermentation - .This study characterized microbial communities from the anoxic layers of the meromictic and sulfidic Fayetteville Green Lake (FGL), NY, United States, and investigated the roles . The final acceptor for its electrons during fermentation is a derivative of pyruvate, such as acetaldehyde during alcohol fermentation, or pyruvate itself during lactic acid fermentation. The final acceptor for electrons during aerobic respiration is oxygen. . The final electron acceptor is NADP. In oxygenic photosynthesis, the first electron .In the absence of any suitable electron acceptor, they use fermentation pathways. In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis and fermentation reactions occur in the cytoplasm. The remaining pathways, starting with pyruvate . Organisms carrying out fermentation, called fermenters, produce a maximum of two ATP molecules per glucose during glycolysis. Table 7.4.1 7.4. 1 compares the final electron acceptors and methods of ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, and fermentation. Note that the number of ATP molecules shown .49 Fermentation: an anaerobic process . In aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain is an oxygen molecule, O 2.If aerobic respiration occurs, then approximately 30 molecules of ATP will be produced during the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis using the energy from the high-energy electrons carried by .
what is the terminal electron acceptor in fermentation pathways? pyruvate or derivative. what are 6 end products of fermentation? lactic acid, ethanol, butyric acid, propionic acid, 2-3-butanediol, mixed acids. describe the end product of fermentation, ethanol (3) -pyruvate loses CO2. -NADH --> NAD+. In humans, the terminal electron acceptor in respiration is always oxygen, which is reduced at complex IV in the respiratory chain. Alternative electron acceptors are mostly found in bacteria and archaea. . Bruce D. Fisher here "the terminal electron acceptor in fermentation, is pyruvate or a pyruvate derivative" And as the . The chemical reactions of lactic acid fermentation are the following: Pyruvic acid + NADH ↔ lactic acid + NAD +. Figure 7.14.1 7.14. 1: Lactic acid fermentation: Lactic acid fermentation is common in muscle cells that have run out of oxygen. The enzyme used in this reaction is lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). The reaction can proceed in either . in the fermentation. What is the terminal electron except er is it stripped right? Comes oxides or and organic compounds. So fermentation, this is what you use if you cannot carry out the TCS cycle and electrical sport game, maybe you don't have a transport game because you're a very simple organism. So this is and an Arabic.The type of terminal electron acceptor [Fe(III), SO 4 2–, S 0] only accounted for 10% of the observed variation in community structure across samples, but the interaction between organic electron donors (i.e., carbon source) and terminal electron acceptors explained an additional 32% of the variation (PERMANOVA interaction term R 2 = 0.321, p .Processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH are collectively referred to as fermentation. In contrast, some living systems use an inorganic molecule as a final electron acceptor; both methods are a type of anaerobic cellular respiration. Anaerobic respiration enables organisms to convert energy for their use in the .
In aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is an oxygen molecule, O 2.If aerobic respiration occurs, then ATP will be produced using the energy of the high-energy electrons carried by NADH or FADH 2 to the electron transport chain. If aerobic respiration does not occur, NADH must be reoxidized to NAD + for reuse as an electron carrier for .

fermentation: Any of many anaerobic biochemical reactions in which an enzyme . is a form of anaerobic respiration that uses carbon as the terminal electron acceptor, resulting in the production of methane. The carbon is sourced from a small number of low molecular weight organic compounds, such as carbon dioxide, acetic .
fermentation: Any of many anaerobic biochemical reactions in which an enzyme . is a form of anaerobic respiration that uses carbon as the terminal electron acceptor, resulting in the production of methane. The carbon is sourced from a small number of low molecular weight organic compounds, such as carbon dioxide, acetic .Oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor in: . Fermentation: A. uses an inorganic molecule as the final electron acceptor B. uses an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor C. produces a large amount of ATP D. is necessary for the production of reduced electron carriers.In lactic acid fermentation the glycolytic product pyruvate is re-used as the final electron acceptor to regenerate the NADH molecule. Pyruvate accepts the electrons from NADH to form lactic acid. Suggest Corrections. 5.terminal electron acceptor in fermentationOxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient.

Figure 6.2.1 6.2. 1: Homolactic (lactic acid) fermentation. Note that the 2 NADH produced in glycolysis are reoxidized to NAD+ when their electrons are added to pyruvate to make the waste product lactate (lactic acid) (2021; Jeanne Kagle) Bacteria of several Gram-positive genera, including Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, and Streptococcus, are .
Cellular respiration begins when electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH 2 —made in glycolysis, the transition reaction, and the Krebs cycle—through a series of chemical reactions to a final inorganic electron acceptor (either oxygen in aerobic respiration or non-oxygen inorganic molecules in anaerobic respiration).
Background Bacillus subtilis is generally regarded as a ubiquitous facultative anaerobe. Oxygen is the major electron acceptor of B. subtilis, and when oxygen is absent, B. subtilis can donate electrons to nitrate or perform fermentation. An anode electrode can also be used by microorganisms as the electron sink in systems called .
terminal electron acceptor in fermentation|what is fermentation in chemistry
PH0 · what is fermentation in chemistry
PH1 · list of electron acceptors
PH2 · final hydrogen acceptor in fermentation
PH3 · final electron acceptor in fermentation
PH4 · final electron acceptor anaerobic respiration
PH5 · electron acceptor molecules
PH6 · Iba pa